ROS Group 产品服务
Product Service 开源代码库
Github 官网
Official website 技术交流
Technological exchanges 激光雷达
LIDAR ROS教程
ROS Tourials 深度学习
Deep Learning 机器视觉
Computer Vision
来退个火吧
-
模拟退火算法是一个非常好用且简单的算法。它的思路也非常简单,下面就介绍一下模拟退火算法。
什么是模拟退火算法呢?
先从这个算法要解决的问题说起。实际上所有的算法都是为了一个目的——从解空间中把解给找出来。最好的当然是找到全局最优解,但是有时候局域最优解也是可以接受的。现在以一个简单的函数求极值的问题作为例子。
如下图这样一个函数,我们要找到其中的最小值。
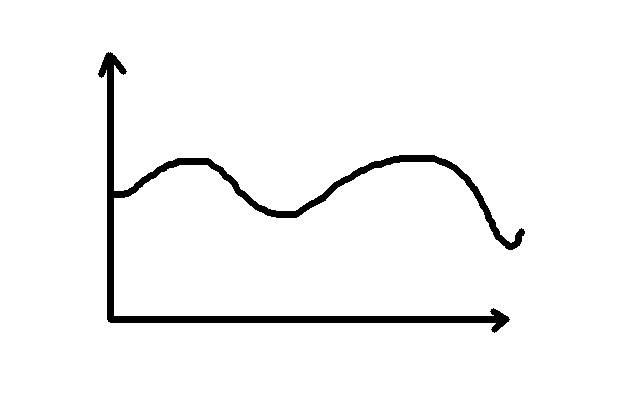
最直接的方法是遍历所有的点。找到其中的最小点。但是很多时候由于解空间太大我们根本没有办法去遍历。这时候就需要高效的算法了。
比较直接的一种算法就是从图上任意一点出发,向两边开始移动,如果新位置的值小于之前位置的值,那么就移动到新的位置。在新位置再重复这个过程,直到无论怎么移动都没有当前的位置的值小的点。可以想象一个小球在曲线上滚动,最终会滚到一个很低的位置。这样我们就不需要遍历所有的点了。但是很有可能我们停在了一个极小值,这个值并不是全局的最有解。上面这个算法就是贪心算法,也叫做爬坡算法。而模拟退火算法就是从这个算法中改出来的。
退火就是金属的冷却过程,刚开始温度比较高,原子运动比较剧烈,随着时间的推移,温度逐渐下降,原子运动也逐渐稳定。而模拟退火就是在模拟这个过程。整体的算法过程和贪心算法一样。但是移动的步长会随着时间在减小。刚开始移动比较剧烈,随着时间的推移每次的移动范围逐渐减小。这样我们就更大的可能性能落在全局的最优点上。而且搜索的速度也要快很多。
下面就是模拟退火算法在小强中的具体应用。
小强的摄像头能够通过SLAM算法得到小强的位置信息,但是这是在摄像头坐标系下的坐标。通常摄像头坐标系和小车坐标系只是差了一个平动和绕竖直轴的转动。但是如果摄像头放歪了,比如向上歪或向下歪。那么小车移动的最终轨迹在摄像头坐标系下就是一个倾斜的平面。我们要在这个平面内画出目标的导航轨迹,首先就要把这个轨迹放平。那就要知道轨迹平面的法向量。怎么计算这个法向量呢?
我们对这个问题进行数学抽象。三维空间有很多点,这些点大致的分布在一个平面上,我们要找到这个平面的法向量。
最直接的方法就是,利用三点确定一个平面的方式,计算出所有点在平面的组合,然后计算这些平面的平均法向量, 类似于最小二乘法的过程。但是如果有上千个点的话,这个计算量就能达到100010001000。
如果采用模拟退火算法的话就很容易了。
我们开始随便取一个法向量方向,然后计算所有点和法平面的距离。如果我们法向量取得好的话,那么所有点到法平面的距离应该差不多。我们可以通过计算这些距离的方差来描述这个差别。
计算一次之后,我们对当前的法向量进行一次随机的转动,然后用新的法向量再次计算这个方差。如果新的方差更小,我们就用新的法向量进行下一次计算。直到计算出比较满意的结果。下面就是具体的计算代码
var getDirection = (pointsList) => { var noUpdateCount = 0; var direction = null; var planePoint = [0,0,0]; // 计算这些点的中心点 for(let pointIndex in pointsList){ planePoint[0] += pointsList[pointIndex][0]; planePoint[1] += pointsList[pointIndex][1]; planePoint[2] += pointsList[pointIndex][2]; } planePoint[0] = planePoint[0] / pointsList.length; planePoint[1] = planePoint[1] / pointsList.length; planePoint[2] = planePoint[2] / pointsList.length; // 计算评价函数 var res = 0; var planeDirection = [Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random()]; // 刚开始的随机方向 planeDirectionLength = distance3d(planeDirection, [0,0,0]); planeDirection = [planeDirection[0] / planeDirectionLength, planeDirection[1] / planeDirectionLength, planeDirection[2] / planeDirectionLength]; // 归一化 let scale = 0; let calcCount = 0 while(noUpdateCount < 5 || scale < 1000){ // 结束条件 scale += 1; // 小转动 var rotation = new THREE.Euler( Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI * Math.exp(- scale / 100), Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI * Math.exp(- scale / 100), Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI * Math.exp(- scale / 100), 'XYZ' ); var currentVector = new THREE.Vector3(planeDirection[0], planeDirection[1], planeDirection[2]); var currentPlaneDirectionVector = currentVector.applyEuler(rotation); var currentPlaneDirection = currentPlaneDirectionVector.toArray(); let currentRes = valueFunc(pointsList, currentPlaneDirection, planePoint); //计算评价函数 if(res == 0 || currentRes < res){ // 找到了更好的解 res = currentRes; // 用新解替换旧的值 planeDirection = currentPlaneDirection; console.log('scale', scale); console.log('res', res); noUpdateCount = 0; }else{ noUpdateCount += 1; } } //保证法向量朝上 if(planeDirection[2] < 0){ planeDirection[0] = -planeDirection[0]; planeDirection[1] = -planeDirection[1]; planeDirection[2] = -planeDirection[2]; } return planeDirection; } function calPointToPlaneDistance(planeDirection, planePoint, targetPoint){ return Math.abs(planeDirection[0] * (targetPoint[0] - planePoint[0]) + planeDirection[1] * (targetPoint[1] - planePoint[1]) + planeDirection[2] * (targetPoint[2] - planePoint[2])); } function valueFunc(pointsList, planeDirection, planePoint){ var res = []; for(let pointIndex in pointsList){ res.push(calPointToPlaneDistance(planeDirection, planePoint, pointsList[pointIndex])); } return diffSq(res); } function diffSq(data){ let total = 0; for(let dataIndex in data){ total += data[dataIndex]; } let avg = total / data.length; let res = 0; for(let dataIndex in data){ res += (data[dataIndex] - avg) * (data[dataIndex] - avg); } return res; } function distance3d(pos1, pos2){ return Math.sqrt((pos1[0] - pos2[0]) * (pos1[0] - pos2[0]) + (pos1[1] - pos2[1]) * (pos1[1] - pos2[1]) + (pos1[2] - pos2[2]) * (pos1[2] - pos2[2])); }运行效率也是不错的
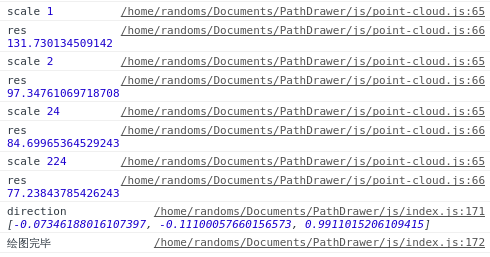
最后法向量的值也是比较准的。看来摄像头基本没有倾斜,摄像头坐标系基本和小车本体坐标系是重合的。